Future Of Art With Generative Ai
Sep 07, 2023 | Aaron Borges
 The convergence of art and technology has always been a catalyst for innovation, redefining the boundaries of human creativity. In recent years, the emergence of generative artificial intelligence (AI) has opened up exciting possibilities for the future of art. This introduction explores the transformative potential of generative AI in the art world, delving into the underlying technical concepts, algorithms, and implications that are reshaping artistic creation.
Generative AI refers to the use of advanced algorithms and computational models to autonomously generate original and unique content. Through the utilization of techniques such as deep learning, neural networks, and machine learning, generative AI algorithms can analyze vast repositories of artistic data, ranging from paintings and sculptures to music and multimedia. By discerning patterns, styles, and semantic relationships within this data, generative AI algorithms can create new and innovative artistic expressions that push the boundaries of human imagination.
Generative AI is not limited to static forms of art. It has also paved the way for interactive art installations and dynamic collaborations between human artists and AI systems. Artists can design installations that respond in real-time to viewer interactions, creating immersive and personalized visual experiences. This collaboration between human creativity and generative AI systems unleashes a realm of innovative possibilities where the lines between the artist and the AI become blurred.
The convergence of art and technology has always been a catalyst for innovation, redefining the boundaries of human creativity. In recent years, the emergence of generative artificial intelligence (AI) has opened up exciting possibilities for the future of art. This introduction explores the transformative potential of generative AI in the art world, delving into the underlying technical concepts, algorithms, and implications that are reshaping artistic creation.
Generative AI refers to the use of advanced algorithms and computational models to autonomously generate original and unique content. Through the utilization of techniques such as deep learning, neural networks, and machine learning, generative AI algorithms can analyze vast repositories of artistic data, ranging from paintings and sculptures to music and multimedia. By discerning patterns, styles, and semantic relationships within this data, generative AI algorithms can create new and innovative artistic expressions that push the boundaries of human imagination.
Generative AI is not limited to static forms of art. It has also paved the way for interactive art installations and dynamic collaborations between human artists and AI systems. Artists can design installations that respond in real-time to viewer interactions, creating immersive and personalized visual experiences. This collaboration between human creativity and generative AI systems unleashes a realm of innovative possibilities where the lines between the artist and the AI become blurred. The advent of
generative artificial intelligence (AI) has ushered in a paradigm shift in the
realm of artistic expression, paving the way for an intriguing future at the
intersection of art and technology. This technical article explores the
disruptive potential of generative AI in the world of art, elucidating the
underlying technical concepts, algorithms, and computational methodologies that
are reshaping the landscape of creative endeavors.
1. Generative AI: The
Catalyst for Artistic Evolution
2. Neural Networks
and Deep Learning for Art Generation:
3. Data Processing
and Training
4. Style Transfer and
Hybrid Artistic Expressions
5. Interactive Art
and Collaborative Endeavors
6. Ethical
Considerations and Future Implications
7. Shaping the Artistic Landscape

1. Generative AI-The Catalyst for Artistic
Evolution:
Generative AI, a branch of artificial intelligence, encompasses algorithms designed to autonomously generate innovative and distinct content. Generative AI algorithms employ techniques such as deep learning, neural networks, and machine learning to analyze vast repositories of artistic data. Through this analysis, the algorithms discern intricate patterns, styles, and semantic relationships within the data, enabling the generation of novel and unique artistic expressions. Training generative AI models for artistic evolution requires access to large volumes of high-quality artistic data. Pre-processing techniques, including image augmentation, normalization, and dimensionality reduction, are employed to prepare the datasets for training. These carefully curated datasets are then utilized to train generative AI models using advanced optimization algorithms such as backpropagation and gradient descent. Through this training process, the models learn to capture the intricate patterns, structures, and artistic nuances necessary for generating novel and aesthetically pleasing artworks.

2. Neural Networks and Deep Learning for Art
Generation:
Neural networks and deep learning have
emerged as fundamental components in the field of art generation through the
application of generative artificial intelligence (AI). This technical
explanation explores the role of neural networks and deep learning in the
generation of art, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms and technical
aspects involved.
Deep learning, a subfield of machine
learning, employs neural networks with multiple hidden layers. These deep
neural networks excel at learning complex patterns and capturing intricate
relationships within datasets. They are particularly well-suited for art
generation tasks, as they can extract and represent the nuanced artistic
styles, structures, and characteristics present in training data.
The strength of neural networks and deep learning lies in their ability to learn complex patterns and generate new artistic content. By training on large and diverse datasets, these models can capture the essence of various artistic styles, enabling the generation of novel artworks that possess similar characteristics. Through the interplay of generator and discriminator networks in GANs, or the manipulation of variables in the latent space representation in VAEs, deep learning models produce visually appealing and aesthetically captivating artworks that push the boundaries of human creativity.
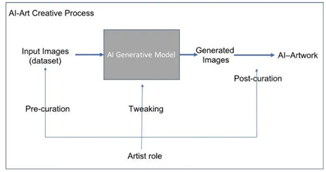
3.
Data
processing and training:
Data processing and training are
crucial steps in the development of generative artificial intelligence (AI)
models for art generation. This technical explanation explores the data
processing techniques and training methodologies involved in harnessing the
power of data for training AI models to create art.
· Data collection
· Pre-Processing
· Feature
Extraction
· Encoding
Once the data is processed, it is
ready for the training phase, where the AI model learns to generate new
artistic content based on the provided dataset. The training process involves
several technical aspects
§
Model Initialization: The generative AI model,
such as a neural network, is initialized with specific architecture and
parameters.
§
Loss Function: A loss function is defined to
measure the discrepancy between the generated output and the target output.
§
Optimization Algorithm: An optimization
algorithm, such as stochastic gradient descent or Adam, is employed to
iteratively update the model's parameters and minimize the loss function.
§
Batch Processing: Training is often performed on
mini-batches of data rather than the entire dataset at once. This allows for
more efficient computation and helps generalize the model's learning across
different samples.
§ Iterative Training: The model is trained through multiple iterations or epochs, where each epoch represents a complete pass through the training data. During each epoch, the model's parameters are updated based on the optimization algorithm, gradually improving the model's performance.

4. Style Transfer and Hybrid Artistic Expressions:
One compelling application of
generative AI in art lies in the domain of style transfer. Employing advanced
neural style transfer algorithms, artists and generative AI systems can
seamlessly blend and transpose artistic styles, giving rise to hybrid art forms.
This technique allows for the fusion of disparate artistic aesthetics while
retaining the fundamental content of the original artwork. Style transfer
offers an unprecedented avenue for experimentation and exploration, enabling
the synthesis of novel artistic styles that transcend conventional boundaries.
Style transfer involves the synthesis of new artworks by combining the content of one artwork with the style of another. This technique allows artists and generative AI systems to blend and transpose artistic aesthetics, resulting in unique and visually compelling compositions. The process of style transfer can be broken down into several key steps.
§ Content and Style Representation: The content and style of the input artworks are represented in a manner suitable for computational analysis.
§
Feature Extraction: Deep neural networks, such
as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), are used to extract content and style
features from the respective artworks
§
Feature Alignment: The content and style
features are aligned to facilitate the blending of styles.
§
Feature Combination: The aligned content and
style features are combined to create a new representation that captures both
the content and the style.
Style transfer enables the creation of hybrid artistic expressions that blend diverse artistic aesthetics. By applying style transfer techniques, artists can explore new combinations of artistic styles, genres, and influences, resulting in visually striking and conceptually innovative artworks.

5. Interactive Art and Collaborative Endeavors
Interactive art refers to artworks
that engage with the viewer, allowing for real-time interaction and
participation. The incorporation of generative AI in interactive art
installations adds a new layer of dynamism and responsiveness to the artistic
experience. Technical components such as sensors, cameras, or motion-tracking
devices can be utilized to capture user inputs or movements, enabling the
artwork to respond and adapt accordingly.
Collaborative endeavors between human
artists and AI systems are another exciting aspect of generative AI in the art
world. Rather than solely relying on AI algorithms to create art, human artists
can enter into a creative partnership with AI systems. This collaboration
allows for a fusion of human creativity and the computational power of AI,
resulting in innovative and boundary-pushing artistic expressions.
Technically, the collaboration between
human artists and AI systems involves a feedback loop. The artist provides
inputs, either in the form of training data, preferences, or guidelines, to the
AI system. The AI system, in turn, generates outputs based on these inputs,
which the artist then evaluates, refines, and integrates into the final
artistic creation. This iterative process allows for a continuous exchange of
ideas and the co-creation of art that combines human ingenuity with the
computational capabilities of generative AI. The technical aspects of
generative AI algorithms facilitate the processing of user inputs, real-time
generation of artistic content, and the co-creation of art that pushes the
boundaries of artistic exploration
6. Ethical
Considerations and Future Implications
The integration of generative
artificial intelligence (AI) in the art world raises important ethical
considerations and carries implications for the future of artistic expression.
This technical explanation explores the ethical considerations associated with
generative AI in art and discusses the potential future implications of its
adoption.
§
Intellectual Property Rights: The use of
generative AI in art raises questions regarding intellectual property rights.
As AI systems generate artworks based on existing artistic styles or datasets,
determining ownership and authorship becomes complex
§
Attribution and Recognition: Attribution of
authorship in AI-generated art poses a challenge. While the AI system performs
the generation process, human artists often provide input, training data, or
artistic preferences
§
Privacy and Data Usage: Generative AI models
rely on large volumes of artistic data for training. The ethical collection and
usage of this data, ensuring privacy rights and consent, are paramount
§
Social Impact: The widespread adoption of
generative AI in art may impact the livelihoods of traditional artists. While
AI-generated art offers new creative possibilities, it is important to consider
its potential effects on the art market
Looking towards the future, the
adoption of generative AI in art holds both promise and challenges:
·
Innovation and Exploration: Generative AI
empowers artists to explore new artistic territories, experiment with novel
styles, and expand their creative boundaries.
· Augmented Creativity: As generative AI becomes more advanced, it can serve as a tool to augment human creativity rather than replace it. Collaborations between human artists and AI systems can lead to new artistic forms
In conclusion, the adoption of generative AI in art necessitates careful ethical considerations and future-oriented planning. Recognizing and addressing issues related to intellectual property, attribution, bias, cultural sensitivity, and privacy is crucial to ensure the responsible and equitable integration of generative AI in the art world.
7. Shaping
the Artistic Landscape
The integration of generative
artificial intelligence (AI) in the art world has the potential to shape the
artistic landscape in profound ways. This technical explanation explores how
generative AI can influence and transform various aspects of the art world,
leading to new artistic forms, experiences, and opportunities.
· Exploration
of New Artistic Frontiers: Generative AI enables artists to explore new
artistic frontiers by transcending traditional boundaries and experimenting
with novel styles, genres, and expressions.
· Democratization
of Artistic Creation: Generative AI democratizes artistic creation by providing
access to tools and technologies that empower a wider range of individuals to
engage in artistic expression.
· Collaboration
between Artists and AI Systems: The collaborative interaction between human
artists and AI systems opens up new possibilities for artistic expression.
· Enhanced
Creativity and Inspiration: Generative AI can serve as a tool for artists to
find inspiration and spark new creative ideas. AI algorithms can generate
alternative artistic possibilities, suggest novel combinations of styles or
elements
· Evolution
of Art Market and Consumption: The advent of generative AI in art has the
potential to transform the art market and how art is consumed. AI-generated
artworks can introduce new forms of artistic expression, challenging
traditional notions of value and authenticity.
Conclusion :
The future of art with generative artificial intelligence (AI) holds immense potential for transformative advancements in the artistic landscape. The integration of generative AI algorithms, such as deep learning models and neural networks, enables the creation of novel and innovative artistic content. By analyzing vast repositories of artistic data, generative AI algorithms can discern intricate patterns, styles, and semantic relationships, pushing the boundaries of human creativity.
Generative AI techniques, such as
style transfer and hybrid artistic expressions, offer new avenues for artistic
exploration and experimentation. The ability to blend and transform artistic
styles, genres, and influences opens up possibilities for the creation of
visually striking and conceptually innovative artworks. Through interactive art
installations and collaborative endeavors, generative AI fosters immersive and
personalized artistic experiences, blurring the boundaries between the artist
and the audience.
In summary, the future of art with
generative AI is characterized by innovation, exploration, and collaboration.
As the art world embraces the possibilities offered by generative AI, it must
navigate ethical considerations and develop frameworks that ensure fairness,
cultural sensitivity, and responsible use. The integration of generative AI has
the potential to shape the future of art, blurring the lines between human
creativity and intelligent algorithms, and ushering in a new era of artistic
expression.
Recommended








