Connecting Rural Artisans With Modern Techniques In Product Design
Mar 13, 2022 | Kshitij Gangurde
 The growing technology has made lives simpler yet more efficient. Organizations and manufacturers are moving towards a more technological approach to producing their products. This helps in various ways, such as increasing the production quantity and the manufacturing speed. The user interfaces of these technologies are also defined and are easy to use and understand for the user. Technology has brought a big revolution in the way products are being made or manufactured, and it has eliminated many manual functions of a process.
Rural artisans perform arts such as Basket making, Handbag weaving, clay handicraft in Bangladesh, Bidriware, carpet weaving, Phulkari, leather handicrafts in India, or Lacquerware, wood and bamboo, metalwork, etc.; in Japan, use handmade techniques to make the handicrafts. Their skills are executed in a delicate way to get a perfect outcome. These handicraft skills have tremendous respect. Many handicrafts are not yet recognized or appreciated. These handmade products describe the culture and the traditions of their place of origin. It has been observed that these handicrafts are vanishing because the artisans and their families aren’t willing to continue the art and shift to other occupations. This major shift is taking place because these arts are not satisfying the financial needs of the artisan families. There aren’t many skilled artisans who can take the traditions forward. These arts need to be saved and taken forward; thus, skilled artisans must perform these arts and continue making handicraft products. The main motive of this research paper is about knowing the traditional techniques of the artisans and studying various product design techniques and creating solutions that can bridge the gap between these two techniques. This paper will include inputs from various interactions with artisans and manufacturers with good questionnaires and responses. This research paper might also have a direct solution of how to adapt modern product design techniques in the process of rural artisans as well.
The growing technology has made lives simpler yet more efficient. Organizations and manufacturers are moving towards a more technological approach to producing their products. This helps in various ways, such as increasing the production quantity and the manufacturing speed. The user interfaces of these technologies are also defined and are easy to use and understand for the user. Technology has brought a big revolution in the way products are being made or manufactured, and it has eliminated many manual functions of a process.
Rural artisans perform arts such as Basket making, Handbag weaving, clay handicraft in Bangladesh, Bidriware, carpet weaving, Phulkari, leather handicrafts in India, or Lacquerware, wood and bamboo, metalwork, etc.; in Japan, use handmade techniques to make the handicrafts. Their skills are executed in a delicate way to get a perfect outcome. These handicraft skills have tremendous respect. Many handicrafts are not yet recognized or appreciated. These handmade products describe the culture and the traditions of their place of origin. It has been observed that these handicrafts are vanishing because the artisans and their families aren’t willing to continue the art and shift to other occupations. This major shift is taking place because these arts are not satisfying the financial needs of the artisan families. There aren’t many skilled artisans who can take the traditions forward. These arts need to be saved and taken forward; thus, skilled artisans must perform these arts and continue making handicraft products. The main motive of this research paper is about knowing the traditional techniques of the artisans and studying various product design techniques and creating solutions that can bridge the gap between these two techniques. This paper will include inputs from various interactions with artisans and manufacturers with good questionnaires and responses. This research paper might also have a direct solution of how to adapt modern product design techniques in the process of rural artisans as well. Introduction
Rural artisans created every essential product such as utensils, shoes, textiles, etc., before the Industrial Revolution in the 18th Century. But then, machines increased the production of goods and were sold on a large scale. This change made it difficult for the local artisans to sell their handmade products. Footwear, textile, furniture, etc., was manufactured in huge bulk in industries. Shoemakers, weavers, ironsmiths, etc. lost a huge part in the market, eventually leading to financial losses to the handicraft industry. Since then, artisans have been leaving handicrafts in the long run. Artisans and their families look up to other jobs and consider handicrafts a secondary option. This results in the vanishing of many handicrafts and their associated traditions. There are synthetic material products that are being replaced for handicraft products. Handicraft employs a vast segment of the craftsperson in rural and semi-urban areas. It is also a major tourist attraction in many parts, such as the blue pottery in Jaipur, Bulgarian craft in Europe, Thai silk in Thailand, etc.
Thus, tourists visit these artisans, and that becomes a source of income. Also, due to the minute detailing, the sustainability cycle, and a showcase of cultural heritage, handicrafts have been exported on a large scale, a developing market. Whereas many handicrafts are not even recognized beyond a few country areas. The artisans have very old skills that they practice. These artisans have their economic status very low; this makes their marketing skills weak at trading. These artisans are not well educated, and thus their connections with any local institutions are either non-existent or weak. Their weak communication skills also are a setback in trading on large scales. These artisans are not aware of modern trends or the latest technologies that can help them expand their small-scale businesses. They are not even used to the social market or the E-commerce platforms. These factors are affecting the success of the rural artisans. The artisans should get exposure to the market through development programs. This will educate them about the new technologies and the market needs. They should be made aware of the user behavior which will help them sell their hand-crafted products on a wider scale.
There is technical equipment that converts the handmade/ manual process into a mechanical one. This helps in manufacturing products more efficiently than handmade processes. Mat weaving or other textile products are being made using big weaving machines in very little time. These machines are costly and thus can’t be afforded by the rural artisans. Similarly, ornaments, footwear, utensils, etc. Have been taken to the industrial levels and are manufactured using heavy machines for more production. This technological growth reduces the opportunities for rural artisans and their products in the market. There is a scope in developing technology products that can be easily usable and affordable for rural artisans. These advanced products can help the artisans in producing handicrafts more efficiently. This will evolve the handicraft market and expand the opportunities for the artisans in rural areas.
Around the globe, there are around 200 million artisans who perform various crafts using leather, textile, metals, wood, glass, paper, plants, or other materials. This huge population follows the art that the generations have practiced before them for centuries. They have gained a certain skillset which gives an artwork of premium quality. The artisans sell these artworks for their income. Various brands tie-up with these artisans to create a remarkable product and sell. Louis Vuitton is known for its elegant and premium quality products all over. Skilled artisans make authentic Louis Vuitton bags. These products are sold at a high price range and recognize an art form.
Similarly, ‘Amazon Handmade’ is also a platform for artisans who want to sell their handcrafted products on a wider platform. This platform has categories from jewelry clothing to home essentials. Many platforms such as ‘okhai.com,’ ‘theindianhouse.com,’ ‘shop.gaatha.com,’ etc., help artisans showcase their work to a bigger audience. This awareness helps in attracting customers and sale of various handicrafts.
Artisans have been using traditional techniques to make handcrafted products. Their hand skills are remarkable and a reason for the art’s legacy. Some craft techniques have also been added to many schools’ curricula to make the students aware of the craft and its tradition.
1) Arnamula mirror is a craft of making metal mirrors that originated in Kerala. This mirror is made from a metal alloy, which is a combination of copper and tin. The artisans extensively polish the surface of this metal alloy for several days to attain sharp reflections. This is a front surface reflection mirror that avoids secondary reflections. In a regular mirror, when an object is touched to the mirror, there is always a gap observed between the object and its reflection. Arambula mirror doesn't have that gap with the reflection of an object. This mirror is considered auspicious and is known for its royal appearance.
Similar handicraft is practiced in Egypt and China. Egyptian artisans practice this art calling it Bronze mirror, which preceded the glass mirrors today. Bronze mirrors were made in China and were known as Chinese magic mirrors. These were used in western countries till the glass mirror came. This art is also vanishing and has become a heritage. A few artisans of the extended families in Arnamula, Kerala, it is only followed by a few artisans.
The first step of making the Arnamula mirror is a design of the mirror's frame is created on paper and then made with a metal sheet. The void for the mirror is left open. With the size of the void, a mold is created to fit a mirror. Tin and copper are added proportionally and heated up to 400° C in an open pit furnace. After it melts, the mixture is poured into the mold. Once it cools down, the mold is broken, and the piece is removed. It is cut into a finished shape, and then it is polished for several days before fitting it into the frame.
2) Wood carving is a form of woodwork where the wood is carved using a sharp tool and chisel. Wood Handicrafts are practiced in various parts of the world with different techniques and different types of wood. Some methods followed are chip carving, whittling, relief carving, Chainsaw carving, etc. Techniques such as embedding or embossing patterns, blocking, surfacing, etc are used to carve. Several types of carving knives are used with different blade features for different purposes of carving. Ornate table makers in Ladakh, Channapata toys in Karnataka, Thanjavur wood carving, European wood carving is a very detailed minute carving of structures practiced in Germany, Italy, Russia, and France.
3) Filigree is practiced in Italian, Portuguese, French, and Indian metalwork. This is an art form to create jewelry using silver or gold. A metal wire is used to make this art using tweezers and chisels. Artisans are sensitive to the designs they create, which their customers always appreciate. Five or more metal threads are held together and turned to soldered back at the meeting ends. A sketch is made of the design, and the threads are turned and soldered. After it cools, it is turned and twisted to get the desired shape. It is again soldered wherever required and then hammered to make it flat. This piece is polished and finished. This process takes a day and patience to detail the smallest feature of the ornament designed by the artisans.
The handloom industry of India has its major chunk into the carpet industry. Around 2.5 million artisans are involved in carpet making. The carpet industry has the maximum export demand in India. Yarn which is made of wool is used to make a carpet. Handloom, broadloom, scrapping machines, finishing machines are the major tools used in the production of carpets. Various knives or other hand tools are used while making the knots. Natural dyes are used to color the wool. The wool is washed and dried. It is then detangled and cleaned to intermix the fiber to make the sheet through spinning. The yarn is colored using natural dyes. The desired design is made and then knotted and weaved on the sheet. The extra threads are then trimmed to attain a better finish. It is later washed and given the last finishing touch. Then it is quality checked and packed for selling. Many other handicrafts have different tools and techniques. These techniques have been practiced with very small modifications in the tools used. Due to industrialization, many manufacturing processes are becoming easier. Similarly, new technologies and machines have been created to covert handmade techniques to machinery. This is increasing the production of handmade products on machines. The efficiency of producing the products by these machines is higher than artificial.
The three major modern manufacturing methods used to create handicrafts are:
a) Layered manufacturing
b) Laser cutting
c) CNC cutting
Layered Manufacturing: Layered manufacturing is another name for 3D printing. 3D printing is widely used to create rapid prototypes of small parts in automotive spaces, etc. This technique works from an input command given to a computer. Layered manufacturing is possible in ABS, PLA, PVA, and polycarbonate materials. Metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, nickel, cobalt-chrome, and titanium alloys can be done using selective laser sintering in the machine. Using this technique, parts of jewelry, décor, ornaments, etc., can be produced. The process for this would require a 3D model of the design in specific formats, and a 3D printer will execute the design in a short period. Once the product is printed, it is finished and assembled to make the final outcome.This takes less time and effort than the handmade process. An industrial Layered manufacturing machine costs around $75,000, whereas a personal 3D printer costs around $300 to $700. There is an additional cost for every material used.
Laser cutting: This is a technique where the material is cut using a high-powered laser beam. This is a costly technique and also hazardous for the environment. Materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, mild steel, titanium, plywood, epoxy, etc., can be cut sliced through this technique. Laser cutting is used for industrial purposes such as cutting flat sheets, and it is also used in small-scale businesses to prototype and make quick models. A CAD/ G-code of a particular design or pattern is given as an input to the computer to obtain the desired shape on a flat sheet. The created design can be assembled by joining the parts to create a product. Using plywood or other metals, small products can be created, such as desk organizers, office essentials, tech accessories, etc. This machine costs around $2,500 to $30,000, varying to the range of the features.
CNC Cutting – This is a subtractive method of shaping a product. This technique uses three axes with tools removing the material from the subject. Live operators are required to guide the axis or set the tools in this machine. Also, a numerical command is given to the machine that automates the cutting process. This technique can work on a wide range of materials like wood to steel. Wood carving, metal handicrafts, or any other solid material crafting can be done using this technique. Different CNC machines are lathe, CNC mills, Plasma cutter, Electric discharge machines (EDM), and water jet cutters. This is a very efficient method of cutting or carving tools, and less time is consumed than handmade processes. The approximate costs of a CNC milling machine are $25,000 to $50,000. These machines require space, time, and cost to function. All artisans can not afford this heavy equipment. Also, these machines need special knowledge to use, and there are various diplomas for teaching the same. Thus, there is a gap between the artisans and modern techniques of manufacturing products. Weaving handicraft is practiced in various countries such as Germany, France, China, Jordan, India, etc. The conventional techniques of weaving are practiced on a drawloom. Two different threads are interlaced on a right angle to make a textile using handmade weaving processes. Other processes are knitting, felting, braiding, crocheting, and plaiting. Using these techniques, artisans create clothes, curtains, bedsheets, denim, towels, rugs, baskets, and other decorative items. People across the world are attracted to these hand-woven products.
Jet air-loom technology is used for more efficient and faster production of textiles. An air-jet loom is a shuttleless loom that uses a jet of air to throw the weft yarn through the warp shed. It is one of two types of fluid-jet looms, the other is a water-jet loom, which was developed earlier. Fluid-jet looms can operate faster than rapier looms(Not commonly used). Air-jet weaving consists of the main nozzle, relay nozzles, and a profiled reed. This makes industries capable of producing good quality textile products quickly.
This has become an attraction to the people and is investing in these processes. Similarly, wood handicraft which was practiced by the greatest number of artisans around the globe using simple tools such as chisel and hammer is overtaken by CNC machines. These take fewer human efforts but give a better outcome quickly. Glassware handicrafts are also depleting because of the introduced glass cutting and molding technologies.Clearer and modernized designs have been created using these glass machines.
Bamboo Handicraft is practiced across the world. Products such as furniture, cutlery, cages, toys, construction purpose, etc., are handcrafted using bamboo. Bamboo cultivation is majorly practiced in Asian countries, resulting in a huge market for bamboo handicrafts. Japan, China, Indonesia, the Philippines, and India broadly practice bamboo handicrafts. Each country practices this craft with different techniques. Here is an overview of some of the efficient techniques used in bamboo handicrafts.
Lashing Bamboo Techniques
Products made out of bamboo have different attachments and joineries. The lashing technique is a type of joinery used in bamboo handicrafts, mostly in Japan and Indonesia. Wrap and a frap are two important techniques used in lashing. Wrapping is the process of drilling a hole and binding the bamboo with a rope or any other similar material. Frapping is the process of winding the binding material (rope) to itself. Wrapping binds the two different bamboo poles, and frapping tightens it.
Square Lashing Technique: When two bamboo poles are supposed to be joined at a right angle, the square lashing technique is used. This technique is used only when the joinery is perpendicular to the ground, and if it is diagonal, then the diagonal lashing technique is used.
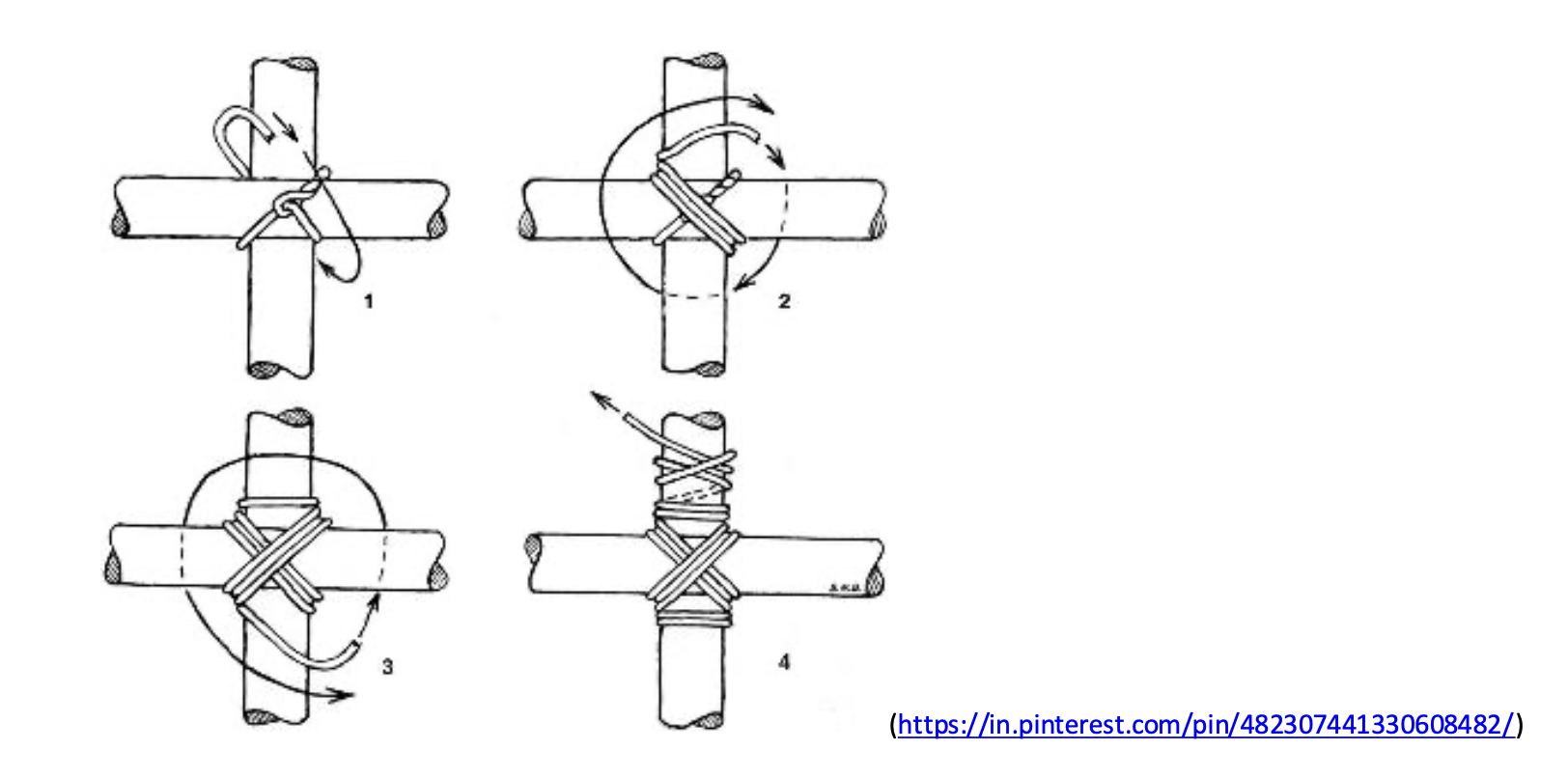
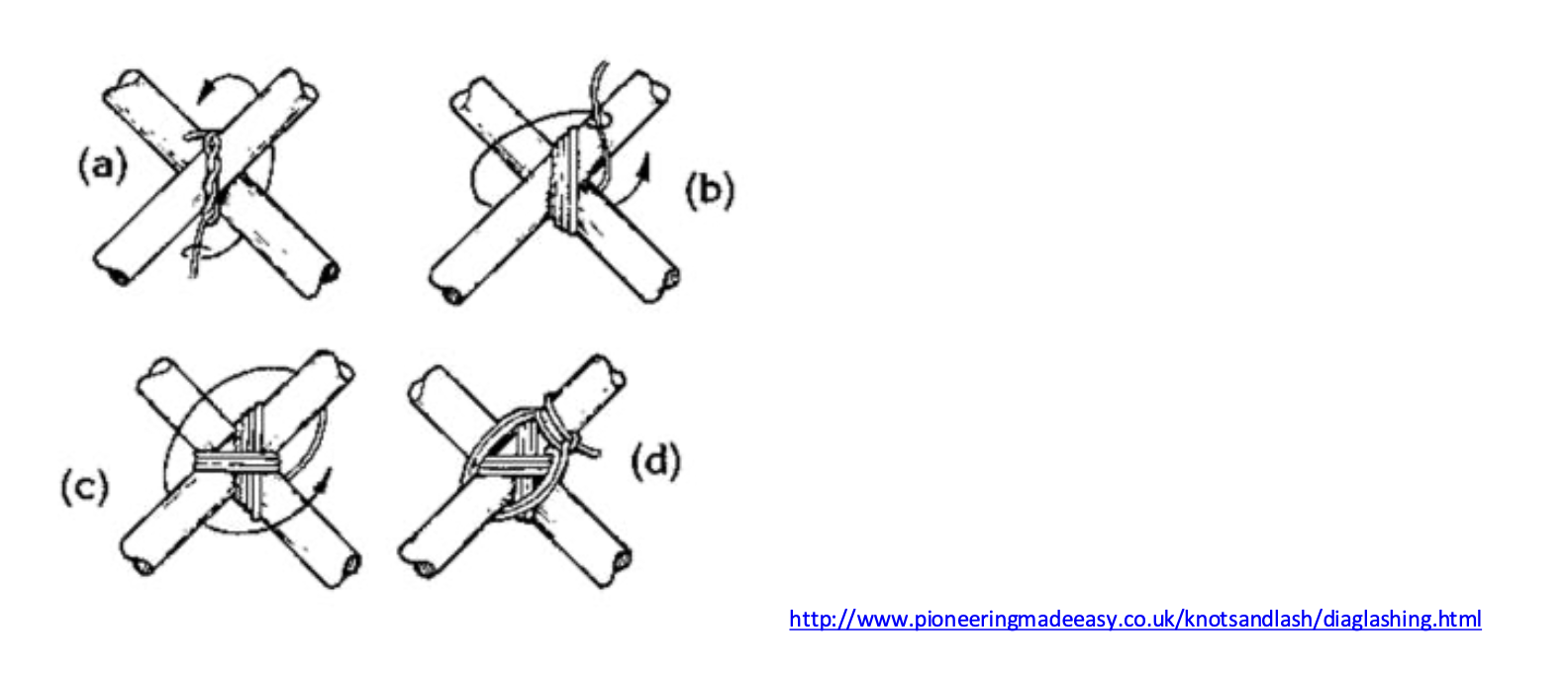
Diagonal lashing technique: The diagonal lashing technique is ground to avoid racking or twisting of the joined poles. An example of this lashing is seen in the crossed legs of the picnic tables.
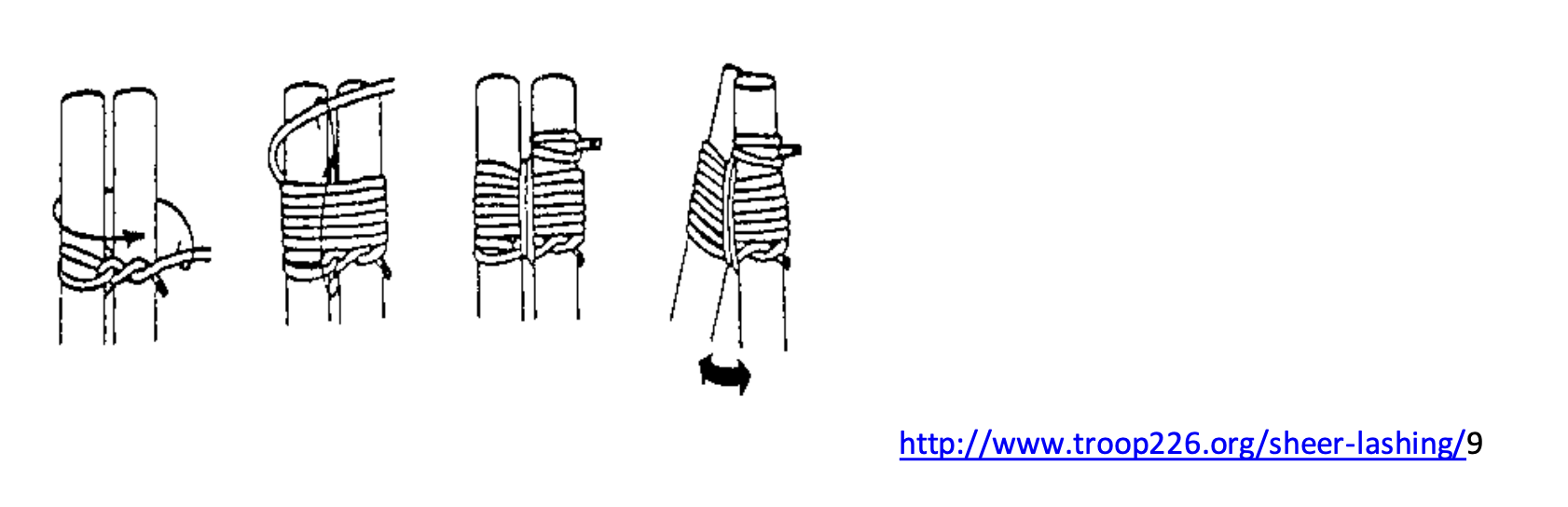
Shear Lashing technique: This technique is used when two poles are supposed to be joined together to form an ‘A-frame structure. The poles are joined parallel initially, and after the joints are tied, the legs can be separated to form the structure.
Peg Lashing Technique and Slant - peg lashing technique – A bamboo peg is inserted in the drilled hole of the pole instead of the lashing or the rope. The rope is then tied to the beg and is made tight binding with the pole. When the joinery is perpendicular to the ground, it is called peg lashing, whereas if it is diagonal to the
Bamboo Handicraft Tools
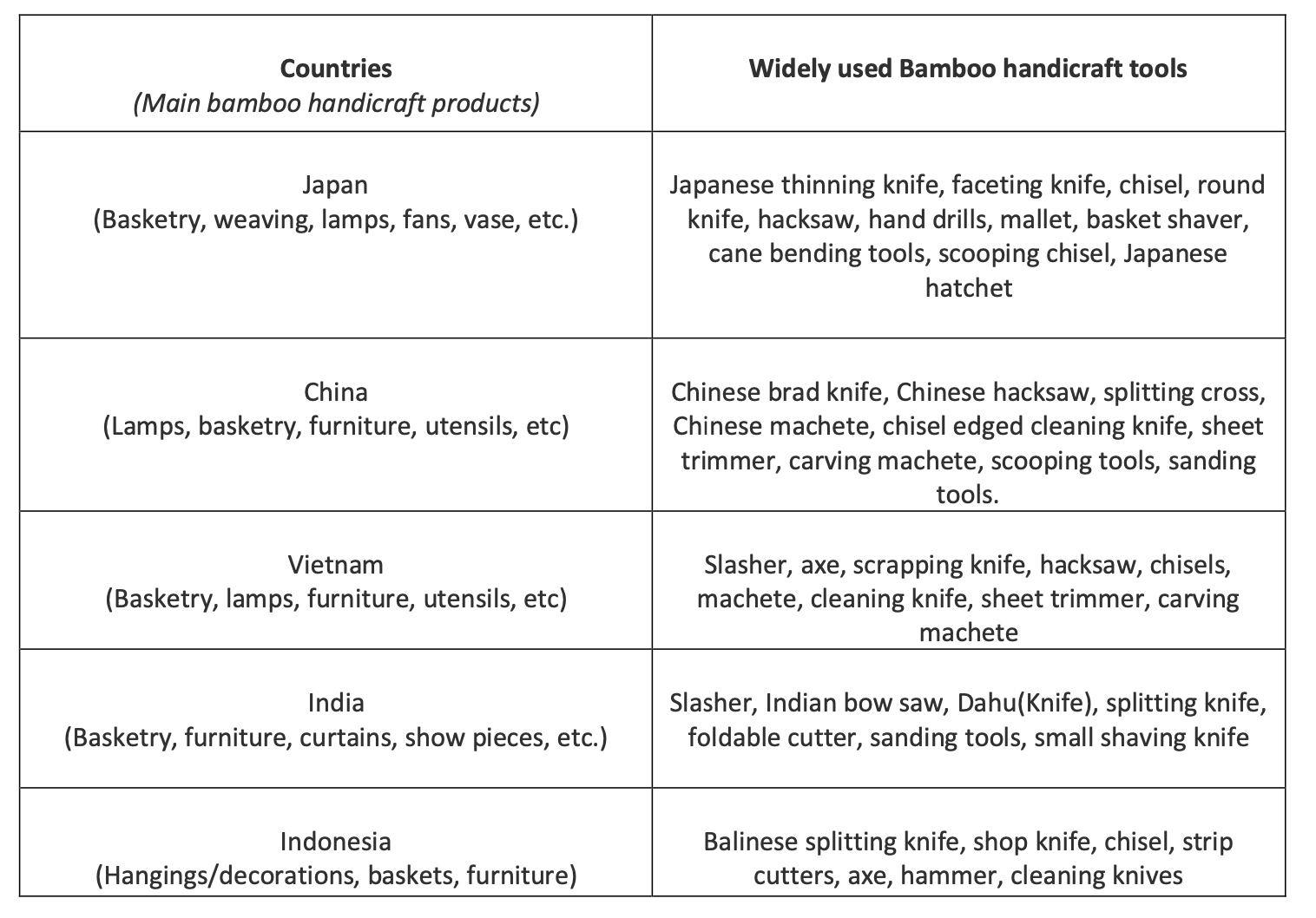
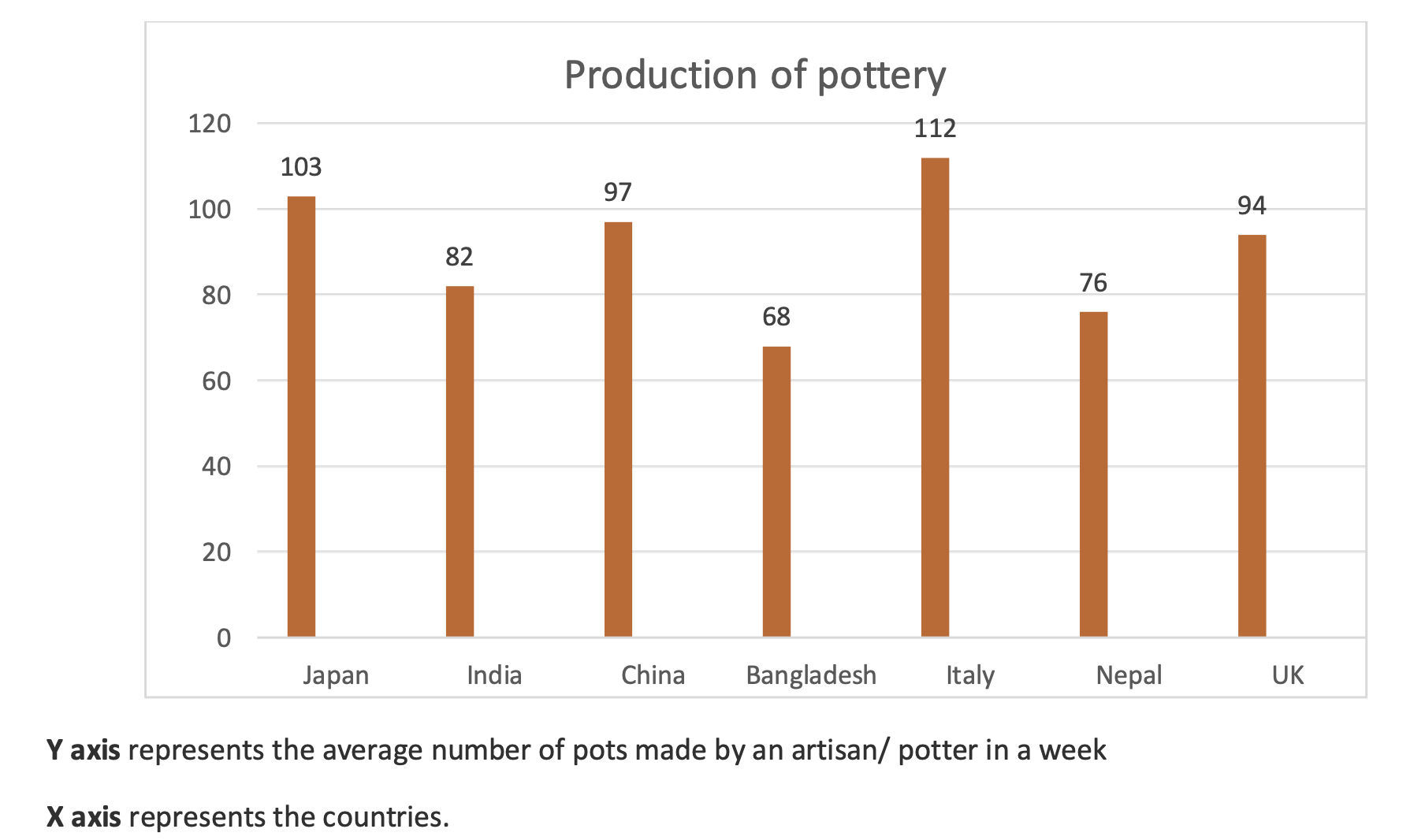
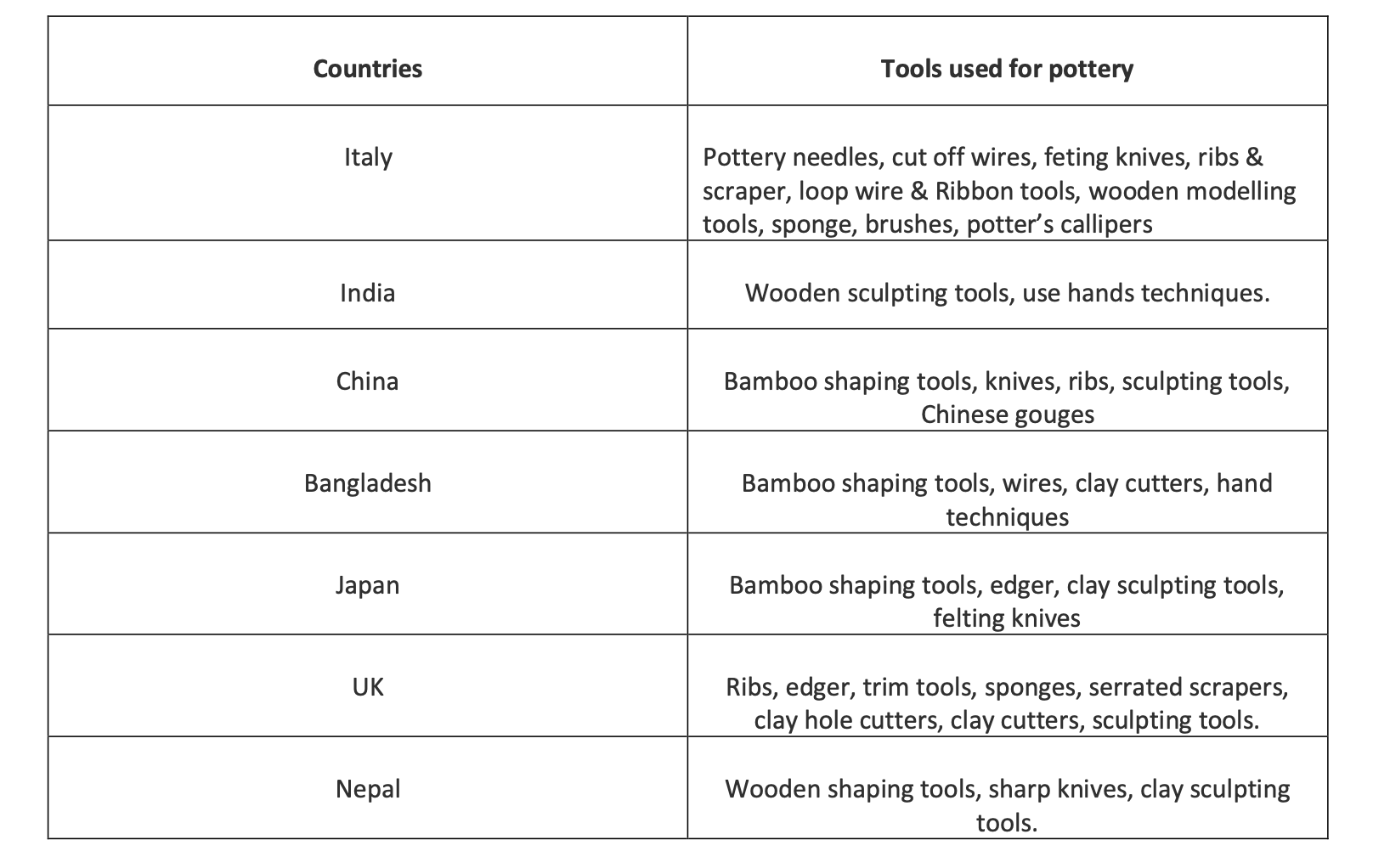
Apart from the joinery techniques, bamboo artisans' tools also impact their work efficiency. Majorly, all the artisans use just one or a limited number of tools to shape the bamboo while making the craft. Indian artisans tend to use one tool for various tasks. Such as, in North-East India, ' Dahu' (A sharp-edged tool with a handle) is used for cutting, sizing, slivering(to cut into small pieces), splitting, and for finishing the bamboo. There are differences in the shape and type of Dahu depending on the region. There is 'Assam Dahu', ‘Tripura Dahu’, ‘Manipur Dahu’, etc. Similarly, 'Kathi' is a cutting tool found in South India and the Northern part. Kathi also has its variations depending on the region. These tools are ergonomic and are easily used by artisans to perform several tasks. However, the efficiency of the workers is less as some tasks require more time, energy, and precision with the same tool. Wood carving tools can't be used for bamboo crafting as the physical properties of both materials is different. Chinese bamboo handicraft artisans use different types of tools as per the task. Tools such as broad Chinese knife, Small splitter, Chinese Cleaning knife, Shaving angle, Strip cutter, sheet trimmer, etc are used by the Chinese artisans. Similarly, Japanese thinning, Faceting, L-shaped saw, etc are used by the Japanese artisans. Using various tools for different tasks makes it easier for the artisan to perform art more effectively with less time and less energy consumption. If these tools are available for the artisans in developing countries such as India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, etc., or other western countries where bamboo handicraft is practiced, it will help the bamboo handicraft industry emerge. If a toolbox is created that contains measuring tools and cutting, scraping, and finishing tools for the artisans, it can be distributed at an affordable price or free of cost under affiliated government benefits. Also, campaigns, where the artisans will be guided through workshops about using the tools, should be held with new tools. This awareness will help them understand and use the tools to make handicrafts more efficient.
Recommended








